Startup Idea Validation: The Ultimate Guide
Startup idea validation represents a systematic methodology for testing business hypotheses before committing significant resources to product development. This process of determining whether a proposed solution addresses genuine market demand and generates sufficient customer interest is crucial to validate a startup idea. The goal is to validate your business idea and ensure your big idea has a real chance.
The validation process encompasses multiple research phases, from initial problem identification through prototype testing and market analysis. Unlike traditional business planning, which relies heavily on assumptions and projections, validation emphasizes data-driven decision making through direct customer interaction and market experimentation.
| Validation Stage | Time Investment | Cost Range | Success Rate |
| Problem Validation | 2-4 weeks | $500-2,000 | 65% |
| Solution Validation | 3-6 weeks | $1,000-5,000 | 45% |
| Product Validation | 6-12 weeks | $5,000-25,000 | 25% |
| Market Validation | 8-16 weeks | $10,000-50,000 | 15% |
Why Validate Your Startup Idea?
Resource optimization drives the primary rationale for startup validation. Entrepreneurs who validate their business ideas reduce development costs by 60-80% compared to those who build products without market confirmation. Validation is the process that helps you avoid wasting time and money on a product no one wants.
The core benefits of systematic validation include:
- Risk mitigation: Test an idea and its assumptions before major capital investment.
- Customer-centric development: Building solutions based on real users’ needs.
- Investor confidence: Demonstrating market demand through empirical evidence.
- Timeline acceleration: Avoiding costly pivots after full product development.
Risk mitigation constitutes another fundamental benefit of the validation process. By testing core assumptions early, startup founders identify potential roadblocks and market resistance before exhausting their initial capital. Companies like Dropbox demonstrated this principle by creating a simple video demonstration to gauge user interest before building their file-sharing platform.
Customer-centric product development emerges naturally from rigorous validation practices. The process forces entrepreneurs to engage directly with their target audience, leading to a deeper understanding of pain points and more precise solution design. This direct feedback loop significantly increases the probability of achieving market fit upon launch.
Idea Validation vs. Market Validation
Idea validation focuses on testing the fundamental problem-solution hypothesis within a specific customer segment. This initial phase examines whether the identified pain point genuinely exists and whether the proposed solution addresses customer needs effectively. Entrepreneurs typically conduct idea validation through surveys, interviews, and basic prototype testing with a small group of potential users.
Market validation is the process that extends beyond individual customer feedback to encompass broader market dynamics, including competition analysis, pricing sensitivity, and scalability potential. This comprehensive evaluation examines market size, customer acquisition costs, and revenue projections to determine commercial viability. This process helps you know if your business idea is commercially sound.
The validation framework progresses logically from idea to market assessment. Successful idea validation provides the foundation for market validation, but positive initial feedback does not guarantee market success. Companies must demonstrate both problem-solution fit and market demand to justify significant investment in product development and business scaling.
Core Startup Validation Methods
Discover the foundational methods to test your business hypothesis, from Lean Startup to Customer Development.
Lean Startup Approach
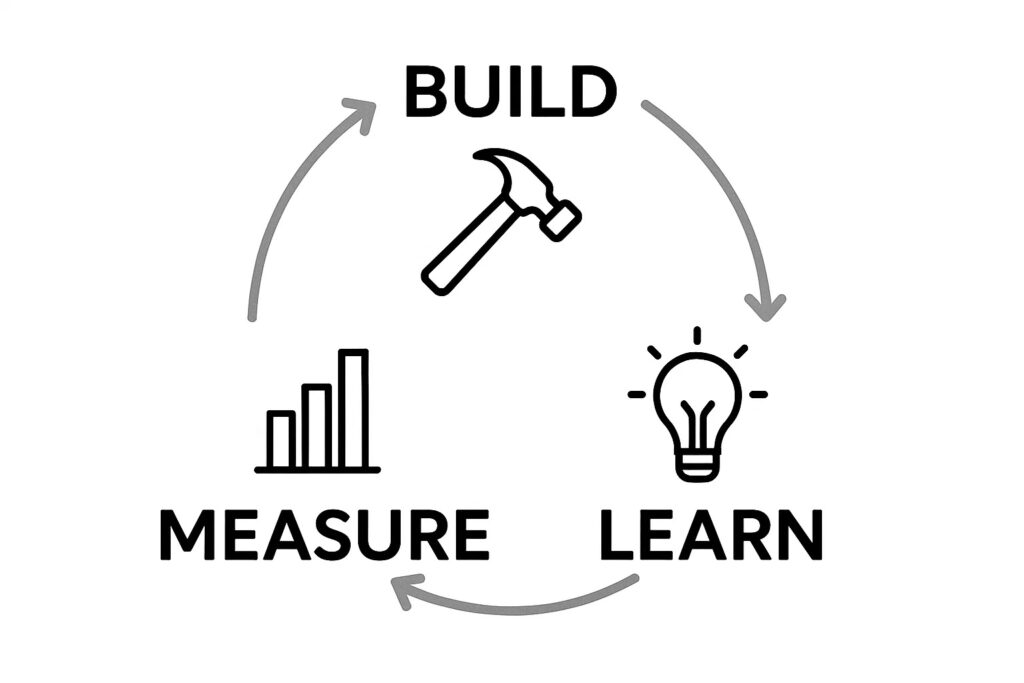
The lean startup methodology, developed by Eric Ries, emphasizes rapid hypothesis testing a startup idea through minimum viable products and iterative development cycles. This approach prioritizes learning over building, encouraging entrepreneurs to test an idea with minimal resource investment before committing to full product development. This is a great way to get early feedback.
Build-measure-learn cycles form the cornerstone of lean startup validation. Entrepreneurs create basic versions of their initial idea, measure customer response through specific metrics, and learn from the data to inform subsequent iterations. This process continues until founders achieve validated learning about their target market and optimal product idea configuration. The new startup Instagram famously pivoted from Burbn after using this approach.
Essential lean startup validation tools include:
- Customer interviews: Direct feedback collection from target users
- A/B testing: Comparative analysis of different solution approaches
- Cohort analysis: Tracking user behavior patterns over time
- Funnel optimization: Improving conversion rates at each customer journey stage
- Pivot assessment: Evaluating when to change direction based on data
Pivot strategies represent a critical component of the lean startup approach. When initial hypotheses prove incorrect, entrepreneurs must decide whether to persevere with minor adjustments or pivot to a fundamentally different business model.
Customer development interviews within the lean framework focus on problem validation before solution development. Steve Blank’s methodology recommends conducting 100+ customer interviews to understand the problem landscape thoroughly before designing any product features. This intensive customer research prevents entrepreneurs from building solutions based on personal assumptions rather than market reality.
Customer Development
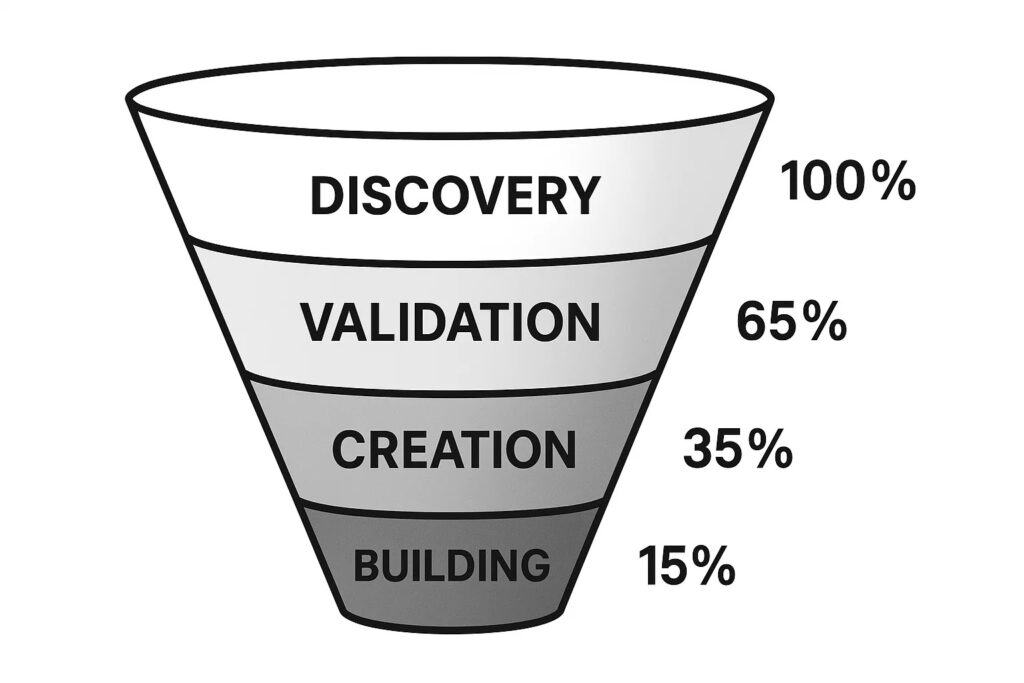
Customer development methodology transforms traditional product development by placing customer discovery at the center of the business creation process. This systematic approach divides startup formation into four distinct phases: customer discovery, customer validation, customer creation, and company building. This is a key step to validate a business idea by truly understanding your customer.
Customer discovery involves identifying and understanding the target customer segment’s specific problems and current solution approaches. During this phase, entrepreneurs conduct extensive interviews with potential customers, observe their behavior patterns, and map their decision-making processes. The goal is to develop deep empathy for customer challenges before proposing any solutions.
Customer validation tests whether the proposed business model can acquire, retain, and monetize customers effectively. This phase typically involves creating basic prototypes or service offerings and measuring customer response through concrete actions rather than verbal feedback. Successful customer validation demonstrates that potential customers will pay for the solution and refer others to the service.
Problem-solution fit measurement requires specific metrics and benchmarks to evaluate customer development progress. Entrepreneurs track indicators such as interview completion rates, problem severity rankings, and willingness to pay statements. These quantitative measures prevent confirmation bias and provide objective assessment of market opportunity.
Practical Validation Frameworks
Explore proven frameworks from HBS and Google to structure your validation process for success.
Harvard Business School Market Validation
The Harvard Business School market validation framework emphasizes rigorous market analysis through a structured five-phase approach: market sizing, competitive analysis, customer segmentation, value proposition testing, and business model validation. This methodology combines academic research principles with practical entrepreneurial application.
| Market Analysis Component | Key Metrics | Data Sources | Timeline |
| Market Sizing | TAM, SAM, SOM | Industry reports, Census data | 2-3 weeks |
| Competitive Analysis | Market share, pricing, features | Company websites, user reviews | 1-2 weeks |
| Customer Segmentation | Demographics, psychographics | Surveys, interviews | 3-4 weeks |
| Value Proposition Testing | Purchase intent, price sensitivity | A/B tests, conjoint analysis | 4-6 weeks |
| Business Model Validation | Unit economics, LTV:CAC ratio | Financial modeling | 2-3 weeks |
Total addressable market calculations provide the foundation for Harvard’s validation approach. Entrepreneurs must demonstrate sufficient market size to support sustainable business growth, typically requiring markets exceeding $1 billion for venture capital consideration. This analysis helps you validate your business idea in a larger market.
Competitive landscape assessment within this framework examines both direct and indirect competitors, analyzing their market positioning, pricing strategies, and customer acquisition approaches. The analysis identifies market gaps and differentiation opportunities while revealing potential barriers to entry and competitive responses to new business entrants.
Customer segmentation analysis divides the target market into distinct groups based on demographics, psychographics, and behavioral patterns. Each segment requires separate validation to ensure the business model works effectively across different customer types. This segmentation often reveals opportunities for market expansion or reveals segments with higher profitability potential.
Failory 4-Step Framework
The Failory idea validation framework streamlines the validation process into four sequential steps to validate: problem validation, solution validation, product validation, and market validation. This systematic approach helps entrepreneurs progress methodically through validation stages while maintaining focus on critical success factors.
Problem validation examines whether the identified pain point represents a genuine market need with sufficient urgency and frequency to drive purchase behavior. Entrepreneurs conduct customer interviews, analyze existing solutions, and measure problem severity through specific metrics such as time spent on workarounds or money currently allocated to alternative solutions.
Solution validation tests whether the proposed approach effectively addresses the validated problem. This phase involves creating basic prototypes, mockups, or service demonstrations to gauge customer response. The focus remains on solution effectiveness rather than full product development, allowing entrepreneurs to iterate quickly based on feedback.
Product validation builds upon successful solution validation by creating functional prototypes that customers can actually use. This phase measures user engagement, retention rates, and satisfaction scores to determine whether the product delivers sufficient value to justify customer acquisition and retention investments.
Market validation encompasses pricing testing, distribution channel analysis, and scalability assessment. Entrepreneurs test different pricing models, evaluate customer acquisition costs, and analyze unit economics to determine commercial viability. This final validation phase provides the data necessary to validate a business idea and attract investment.
Google Design Sprints
Google Design Sprints compress the validation process into intensive five-day workshops that rapidly prototype and test an idea. This methodology combines design thinking principles with rapid experimentation to validate a startup idea before significant development investment. This is a great way to take your startup from a concept to a tested prototype.
The sprint process begins with problem mapping and target selection, where teams identify the most critical business challenge requiring validation. Day two focuses on solution sketching, where participants generate multiple approaches to the identified problem. This divergent thinking phase prevents premature convergence on suboptimal solutions.
Prototype development during days three and four creates realistic product demonstrations that customers can interact with and evaluate. These prototypes prioritize customer-facing features over technical functionality, enabling rapid creation and testing. The emphasis on facade-level prototyping allows teams to test an idea without backend development.
Customer testing on day five provides direct market feedback through structured user interviews and usability testing sessions. Teams observe customer behavior, measure task completion rates, and gather qualitative feedback about the proposed solution. This concentrated testing of a startup idea yields actionable insights within a single week.
Low-Cost Validation Techniques
Learn how to test your idea with minimal investment using landing pages, prototypes, and network feedback.
The Fake Door Landing Page
Fake door testing represents one of the most cost-effective validation methods, requiring minimal technical resources while providing concrete demand measurement. This technique involves creating landing pages that describe the proposed product idea and measure customer interest through email signups, pre-orders, or feature requests. It helps you validate your idea by seeing if customers are truly willing to pay.
Critical elements for effective fake door landing pages:
- Clear value proposition: Concise explanation of problem and solution
- Specific call-to-action: Email signup, waitlist join, or pre-order button
- Realistic pricing: Market-appropriate cost estimates
- Feature descriptions: Detailed functionality explanations
- Timeline expectations: Honest delivery or launch dates
Landing page design for validation purposes emphasizes clear value propositions and specific call-to-action buttons that simulate actual purchase or signup processes. The page should accurately represent the intended product without misleading potential customers about availability. Effective fake door pages include detailed feature descriptions, pricing information, and timeline expectations.
Conversion rate measurement provides quantitative validation data for entrepreneurial decision-making. Industry benchmarks suggest that landing page conversion rates above 2-3% for email signups indicate genuine market interest, while conversion rates below 1% typically suggest insufficient demand or poorly communicated value propositions. This helps you know if your business idea has support for the idea.
Traffic generation for fake door testing can utilize multiple channels, including social media advertising, content marketing, and personal networks. The key is generating sufficient traffic volume to achieve statistical significance in conversion measurements. Entrepreneurs should target at least 1,000 unique visitors to draw meaningful conclusions from fake door experiments.
Early Feedback from Your Network
Network-based validation leverages existing personal and professional relationships to gather initial idea feedback with minimal cost and maximum trust. This approach provides rapid access to potential customers who are willing to provide honest feedback about proposed business concepts. This is one of the quickest steps to validate your concept.
Systematic network outreach involves creating structured interview protocols that gather consistent information across multiple conversations. Entrepreneurs should prepare specific questions about problem severity, current solution approaches, and willingness to pay for improved alternatives. This structured approach prevents confirmation bias and ensures comprehensive data collection.
Feedback quality varies significantly across different network segments, with professional contacts typically providing more relevant business insights than personal friends and family members. Industry colleagues, former clients, and professional association members often deliver more actionable feedback about market dynamics and competitive considerations.
Network feedback limitations include potential bias toward positive responses and limited market representation. Most personal networks exhibit demographic and psychographic similarities that may not reflect broader market diversity. Entrepreneurs must supplement network feedback with broader market research to validate assumptions across different customer segments.
Prototype & MVP
Minimum viable product (MVP) development focuses on creating the smallest possible version that demonstrates core value propositions to target customers. This approach emphasizes functionality over polish, enabling rapid market testing a startup idea with minimal development investment. This is a great way to validate your idea and see if it works.
Prototype testing methodology involves structured customer interactions that measure both usability and value perception. Entrepreneurs should observe customer behavior during prototype use, tracking task completion rates, error frequencies, and time-on-task metrics. These quantitative measures complement qualitative feedback about user experience and perceived value.
Iterative development cycles allow entrepreneurs to incorporate customer feedback systematically while maintaining development momentum. Each iteration should address specific customer pain points identified during previous testing phases. This approach prevents feature creep while ensuring that product development remains aligned with validated customer needs.
Customer retention metrics during prototype testing provide early indicators of market fit potential. Users who return to use prototypes multiple times or recommend them to others demonstrate genuine value perception. Retention rates above 20% after 30 days typically indicate strong product-market alignment.
Crucial Steps in Any Validation
Master the essential steps of defining problems, testing solutions, and analyzing metrics to avoid common pitfalls.
Define Your Problem
Problem definition requires specific, measurable descriptions of customer pain points rather than vague generalizations about market opportunities. Entrepreneurs must identify who experiences the problem, how frequently it occurs, and what consequences result from the problem remaining unsolved. This specificity enables targeted solution development and accurate validation measurement. This is a fundamental step to validate a startup idea.
| Problem Validation Questions | Purpose | Expected Outcome |
| Who experiences this problem? | Target identification | Specific customer segments |
| How often does it occur? | Frequency assessment | Usage/demand patterns |
| What’s the current solution? | Alternative analysis | Competitive landscape |
| What’s the cost of inaction? | Severity measurement | Value proposition basis |
| When does the problem happen? | Context understanding | Use case scenarios |
Customer interviews for problem validation should focus on past behavior and current solutions rather than hypothetical future preferences. Questions like “Tell me about the last time you experienced this problem” yield more reliable data than “Would you use a product that solves this problem?” Behavioral data predicts future actions more accurately than stated intentions. This helps you know if your business idea is solving a real problem.
Problem severity assessment involves quantifying the impact of identified pain points on customer daily operations, productivity, or satisfaction. Entrepreneurs can measure problem severity through time studies, cost analyses, or satisfaction surveys that establish baseline conditions before solution introduction. This quantitative foundation supports business model development and pricing strategy.
Market size estimation begins with problem prevalence analysis across the target customer segment. Entrepreneurs must determine what percentage of potential customers experience the identified problem with sufficient severity to justify solution investment. This analysis often reveals that initially attractive problems affect smaller market segments than originally anticipated.
Test Your Solution
Solution testing methodology emphasizes customer behavior observation over opinion collection. Entrepreneurs should create opportunities for potential customers to interact with proposed solutions and measure their responses through actions rather than statements. This behavioral focus provides more reliable validation data than survey responses or interview feedback. It’s a great way to test an idea and see how real users react.
A/B testing different solution approaches enables entrepreneurs to identify optimal feature combinations and user experience designs. This comparative methodology helps distinguish between customer preferences and random feedback variations. Statistical significance requires sufficient sample sizes, typically exceeding 100 users per testing variation.
User experience metrics during solution testing include task completion rates, error frequencies, and time-to-value measurements. These quantitative indicators reveal solution effectiveness independent of customer opinions. Solutions that enable rapid task completion with minimal errors typically demonstrate stronger product-market fit potential.
Value proposition communication testing examines whether customers understand and appreciate the proposed solution benefits. Entrepreneurs should measure comprehension rates, feature prioritization, and willingness to pay responses to validate that solution benefits align to your business goals. Misalignment in this area often indicates the need for positioning adjustments or feature modifications.
Analyze Your Metrics
Metric selection for validation analysis should focus on leading indicators of business success rather than vanity metrics that provide limited actionable insight. Key performance indicators typically include customer acquisition cost, lifetime value ratios, retention rates, and referral frequencies. These metrics directly correlate with business model viability and scalability potential.
Essential validation metrics to track:
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): Cost to acquire each new customer
- Lifetime Value (LTV): Total revenue expected from each customer
- Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR): Predictable monthly income
- Churn Rate: Percentage of customers who stop using the product
- Net Promoter Score (NPS): Customer satisfaction and referral likelihood
Statistical significance requirements ensure that validation conclusions are based on reliable data rather than random variations or small sample sizes. Entrepreneurs should establish minimum sample size requirements before beginning validation testing to avoid premature conclusions based on insufficient data. Industry best practices recommend minimum sample sizes of 100-200 participants for most validation experiments.
Cohort analysis reveals customer behavior patterns over time, providing insights into retention trends and usage evolution. This longitudinal analysis helps entrepreneurs distinguish between initial enthusiasm and sustained engagement. Cohort retention rates above 40%
after 30 days typically indicate strong product-market fit potential.
Conversion funnel analysis identifies optimization opportunities throughout the customer acquisition and onboarding process. Entrepreneurs should measure conversion rates at each stage, from initial awareness through active usage and potential referral generation. This analysis often reveals unexpected bottlenecks that prevent customer adoption despite strong initial interest.
Common Validation Pitfalls
Recognize and avoid typical mistakes that can derail your startup, from overbuilding to ignoring customer feedback.
Don’t Skip Customer Conversations
Customer conversation avoidance represents one of the most common validation mistakes, often driven by fear of negative feedback or confidence in personal market understanding. Entrepreneurs who skip direct customer interaction frequently build products based on assumptions that prove incorrect when subjected to market testing. This avoidance typically stems from confirmation bias and overconfidence in personal problem identification. Validation involves talking to real users.
Interview quality matters more than interview quantity in customer validation research. Poorly structured conversations that lead customers toward desired responses provide misleading validation data. Effective customer interviews use open-ended questions and avoid solution-focused discussions during problem exploration phases. The goal is understanding customer perspectives rather than convincing them to validate entrepreneurial assumptions.
Remote interview techniques have expanded access to diverse customer segments while reducing research costs. Video conferencing tools enable entrepreneurs to conduct customer conversations across geographic boundaries and time zones. However, remote interviews require additional attention to engagement maintenance and non-verbal communication observation.
Documentation and analysis of customer conversations prevent important insights from being lost or misinterpreted. Entrepreneurs should record interviews when possible and create structured summaries that identify common themes and contradictions across multiple conversations. This systematic approach reveals patterns that inform product development and market strategy decisions.
Liking Your Idea Is Not Enough
Customer enthusiasm expressed through verbal feedback often fails to translate into purchase behavior or sustained usage. Entrepreneurs must distinguish between polite positive responses and genuine demand indicators. Real validation requires customers to demonstrate value perception through concrete actions such as monetary payment, time investment, or referral generation. Just because someone says they like your initial idea doesn’t mean they’re willing to pay for it.
Social desirability bias influences customer feedback during validation research, with respondents providing responses they believe entrepreneurs want to hear rather than expressing genuine preferences. This bias particularly affects friends, family members, and professional network contacts who may prioritize relationship maintenance over honest feedback. Effective validation methodology accounts for this bias through behavioral measurement rather than opinion collection.
Purchase intent statements during validation research correlate poorly with actual buying behavior across most market segments. Customers frequently overestimate their likelihood of purchasing new products or services when presented with hypothetical scenarios. Entrepreneurs should focus on demonstrated behavior patterns and revealed preferences rather than stated purchase intentions.
Engagement depth provides more reliable validation indicators than superficial positive responses. Customers who ask detailed questions about features, pricing, and availability demonstrate genuine interest that extends beyond politeness. Similarly, customers who volunteer specific use cases or provide detailed feedback about current solutions indicate authentic problem experience.
Overbuilding & Overinvesting
Feature creep during validation phases distracts entrepreneurs from core value proposition testing while consuming limited resources unnecessarily. This tendency often reflects anxiety about product competitiveness or desire to address every piece of customer feedback immediately. Successful validation maintains focus on essential features that demonstrate primary value propositions.
Technical perfectionism during prototype development delays market testing and increases validation costs without corresponding benefits. Entrepreneurs often spend excessive time on technical implementation details that customers cannot perceive or appreciate during validation testing. The goal during validation is demonstrating value propositions rather than creating production-ready systems.
Resource allocation for validation should follow the 80/20 principle, with the majority of effort focused on customer interaction and market testing rather than product development. Many entrepreneurs invert this priority, spending 80% of their time building and 20%
validating, which increases failure risk and resource waste.
Validation budget management prevents entrepreneurs from exhausting startup capital before achieving validated learning about market opportunity. Effective validation typically requires 10-20% of total startup capital, with the remainder reserved for product development and market entry after validation completion. This resource allocation ensures sufficient capital remains available for scaling validated concepts.
When to Move Forward
Decision criteria for transitioning from validation to development should be established before beginning validation activities to prevent subjective interpretation of ambiguous results. Clear success metrics enable objective evaluation of validation outcomes and prevent endless testing cycles that delay market entry without providing additional certainty.
| Validation Success Indicators | Minimum Threshold | Industry Benchmark |
| Customer Interview Completion Rate | 80% | 85-95% |
| Problem Severity Rating (1-10 scale) | 7+ | 8+ |
| Solution Interest Score | 70% | 75-85% |
| Landing Page Conversion Rate | 2% | 3-5% |
| Prototype Retention Rate (30-day) | 40% | 45-60% |
| Willingness to Pay Percentage | 60% | 65-80% |
Product-market fit indicators during validation include consistent positive customer feedback, retention rates exceeding 40%, and organic referral generation. These metrics suggest that the solution addresses genuine market needs with sufficient value delivery to support sustainable business growth. However, entrepreneurs must validate these indicators across representative customer segments rather than limited early adopter groups.
Market timing considerations affect validation interpretation and development decisions. Products that receive positive validation feedback during favorable market conditions may face different reception during economic downturns or competitive intensity changes. Entrepreneurs should consider macroeconomic factors and industry cycles when interpreting validation results.
Investment readiness assessment involves evaluating whether validation results support scalable business model development and investor interest. Venture capital firms typically require demonstrated traction metrics and clear path to significant market penetration before considering investment. Angel investors may accept earlier-stage validation but still require evidence of customer demand and founder execution capability.
Final Thoughts
Validation methodology selection depends on startup characteristics including target market, product complexity, and available resources. B2B startups typically require longer validation cycles with fewer customers, while consumer products can validate through larger sample sizes with shorter interaction periods. Technology products may require functional prototypes, while service businesses can validate through customer interviews and pilot programs.
Common validation methodology combinations by business type:
- B2B SaaS: Customer interviews + fake door landing pages + pilot programs
- Consumer apps: Prototype testing + A/B experiments + cohort analysis
- E-commerce: Market research + competitive analysis + pre-order campaigns
- Marketplace platforms: Two-sided validation + network effect testing
- Hardware products: Prototype validation + crowdfunding campaigns +
manufacturing partnerships
Continuous validation throughout product development maintains market alignment as customer needs and competitive landscapes evolve. Successful entrepreneurs treat validation as an ongoing business process rather than a one-time startup activity. This continuous approach prevents product-market fit deterioration and identifies expansion opportunities as businesses mature.
Validation investment yields significant returns through reduced development risk, improved product-market fit, and enhanced investor attractiveness. Companies that complete thorough validation processes typically raise capital more efficiently and scale more successfully than those that skip validation phases. The upfront time and resource investment in validation prevents much larger losses from building unwanted products.