Problem Slide Pitch Deck: Complete Guide to Creating Impactful Slides That Convert Investors
Investors evaluate hundreds of pitch deck presentations annually, making this slide a critical filter for determining which startups deserve deeper consideration.
This foundational slide serves as the basis upon which your entire business case rests. When investors understand the issue your startup addresses, they can better assess the market opportunity, potential customer base, and revenue projections that follow. Without a compelling statement of customer pain, even innovative solutions fail to secure funding because investors cannot visualize the target audience or market demand.
The role of a problem slide
A well-crafted slide establishes the narrative framework for your entire pitch deck. It transforms abstract business concepts into tangible customer pain points that investors can immediately grasp. The presentation must demonstrate that you possess deep market understanding while positioning your startup as uniquely qualified to address this specific issue.
Within the framework of financial modeling, this slide directly impacts how investors calculate market size and addressable opportunity. When you clearly define customer pain points, investors can more accurately assess the willingness to pay for solutions, customer acquisition costs, and potential market penetration rates.
What investors look for
Investors seek evidence that entrepreneurs have identified an issue worth solving through systematic market research rather than personal assumptions. They evaluate whether the pain points presented affect a sufficiently large target audience to justify significant investment and whether current alternatives inadequately address these challenges.
Key evaluation criteria include:
- Market size validation through quantifiable data
- Customer discovery evidence demonstrating real user interviews
- Competitive landscape analysis showing gaps in existing solutions
- Problem urgency indicators that suggest customers actively seek alternatives
Depending on market conditions, investors may prioritize different aspects of problem validation. During economic uncertainty, they focus heavily on must-have versus nice-to-have problem categories.
Craft a Powerful Problem Statement
Effective definition requires moving beyond surface-level symptoms to identify root causes that create genuine customer frustration. Your statement slide must articulate specific scenarios where your target audience experiences measurable negative impacts from current market conditions or available solutions.
The most compelling statements focus on quantifiable business or personal costs. For B2B markets, this means calculating time lost, revenue missed, or efficiency reduced. For consumer markets, emphasize emotional or financial consequences that motivate behavior change.
Make it relatable
Investors must immediately understand why customers care about solving this particular challenge. Create scenarios that resonate with investor experiences or common business challenges they recognize from their portfolio companies. Use concrete examples rather than abstract concepts to illustrate how these issues manifest in real-world situations.
Successful entrepreneurs often share brief customer anecdotes that highlight the impact without revealing confidential information. These stories should demonstrate customer willingness to invest time, money, or effort in finding better alternatives to current solutions.
Empathize with the target market
Deep customer empathy distinguishes experienced entrepreneurs from those making assumptions about market needs. Your presentation should reflect genuine understanding of customer workflows, decision-making processes, and the specific contexts where pain points become most acute.
This empathy manifests through precise language that mirrors how customers describe their challenges. When you use terminology and examples that resonate with your target audience, investors recognize authentic market research and customer discovery work.
Provide data and facts
Quantitative validation transforms anecdotal challenges into investable market opportunities. Include relevant statistics about issue frequency, current solution costs, or market research findings that support your core statement. However, focus on the most impactful data points rather than overwhelming investors with excessive information.
Credible data sources include:
- Industry analyst reports
- Government statistics
- Academic research studies
- Customer survey results
- Competitive analysis findings
Highlight poor and current alternatives
Demonstrating inadequate existing solutions validates both market opportunity and your startup’s potential competitive advantage. Analyze why current alternatives fail to fully address customer pain points, whether due to cost, complexity, accessibility, or performance limitations.
This analysis should reveal specific gaps your solution will address without immediately jumping into solution details. Focus on what customers currently do to work around these challenges and why these workarounds create additional friction or costs.
Design Your Slide for Impact
Investors spend approximately 3 minutes and 44 seconds reviewing each pitch deck, making concise communication essential for problem slide effectiveness. Each bullet point or sentence must convey maximum information density while remaining immediately comprehensible.
Eliminate unnecessary adjectives and focus on action-oriented language that describes customer behaviors and outcomes. Replace vague terms like “challenging” or “difficult” with specific descriptions of time wasted, money lost, or opportunities missed.
Use visuals to illustrate
Visual elements help investors quickly grasp complex problems that might require lengthy explanations in text form. Effective visuals for problem slides include customer journey maps, before-and-after scenarios, process flow diagrams, or infographics that highlight key statistics.
Charts and graphs should focus on trends that demonstrate growing problem severity or expanding market impact over time. Avoid decorative visuals that don’t directly support your problem narrative or add meaningful context for investor understanding.
Maintain a consistent slide design
Professional presentation design reinforces credibility and makes your content more digestible for investor audiences. Consistent typography, color schemes, and layout structures help investors focus on your message rather than being distracted by design inconsistencies.
Your problem slide design should align with the overall deck aesthetic while using visual hierarchy to emphasize the most critical information. Bold headings, strategic white space, and logical information flow guide investor attention to key pain points.
Separate the problem and solution
Resist the temptation to introduce solution elements within your problem slide presentation. Mixing problem description with solution hints dilutes the impact of both sections and prevents investors from fully appreciating the market opportunity before evaluating your approach.
A dedicated problem slide allows investors to form independent opinions about market size and opportunity before you influence their thinking with your specific solution approach. This separation also demonstrates disciplined thinking and structured presentation skills.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
While data supports validation, overwhelming investors with statistics obscures rather than clarifies your core message. Select the two or three most compelling data points that directly support your statement rather than including every research finding.
Too much information creates cognitive overload and prevents investors from focusing on the essential question: do customers experience significant pain that justifies seeking alternatives? Supporting evidence should enhance understanding without becoming the primary focus.
Being vague or generic
Generic statements that could apply to multiple industries or customer segments fail to demonstrate the specific market knowledge investors expect from serious entrepreneurs. Avoid broad claims about “inefficiency” or “poor user experience” without concrete examples.
Specificity signals deep customer understanding and market research. Instead of stating “small businesses struggle with marketing,” specify “local restaurants lose an average of $2,400 monthly revenue due to inconsistent social media presence during peak dining seasons.”
Neglecting the target audience
Presentations must clearly identify who experiences these pain points and why they represent an attractive customer segment. Failing to define your target audience leaves investors uncertain about market size, customer acquisition strategies, and revenue potential.
Include demographic, psychographic, or firmographic details that help investors visualize your ideal customers. B2B presentations should specify company sizes, industries, and roles of decision-makers who experience the most acute pain.
Not making the problem big enough
Investors seek opportunities with significant market potential, requiring challenges that affect large customer populations or generate substantial per-customer impact. Small-scale issues may warrant lifestyle businesses but rarely justify venture capital investment.
Frame your challenge in terms that demonstrate scalability and market size. Show how solving this issue could impact thousands or millions of potential customers, or how individual customers would pay substantial amounts for effective solutions.
Problem Slide Examples and Templates
Successful startup pitch deck examples provide valuable insights into effective problem presentation strategies. These companies secured significant funding by clearly articulating customer pain points that resonated with investor audiences and demonstrated substantial market opportunities.
Analyzing proven examples reveals common patterns in problem slide structure, messaging approaches, and visual design choices. However, direct copying reduces authenticity – use these examples to understand principles rather than replicate specific content.
AirBNB

Airbnb‘s original slide focused on the friction and cost associated with traditional hotel bookings, particularly for price-sensitive travelers and unique location preferences. They highlighted how existing accommodation options failed to serve travelers seeking authentic local experiences or budget-friendly alternatives.
The company presented specific pain points: high hotel costs in popular destinations, limited availability during peak seasons, and lack of local community connection. Their presentation established clear customer segments (budget travelers and experience seekers) while quantifying the addressable market size.
AirCall
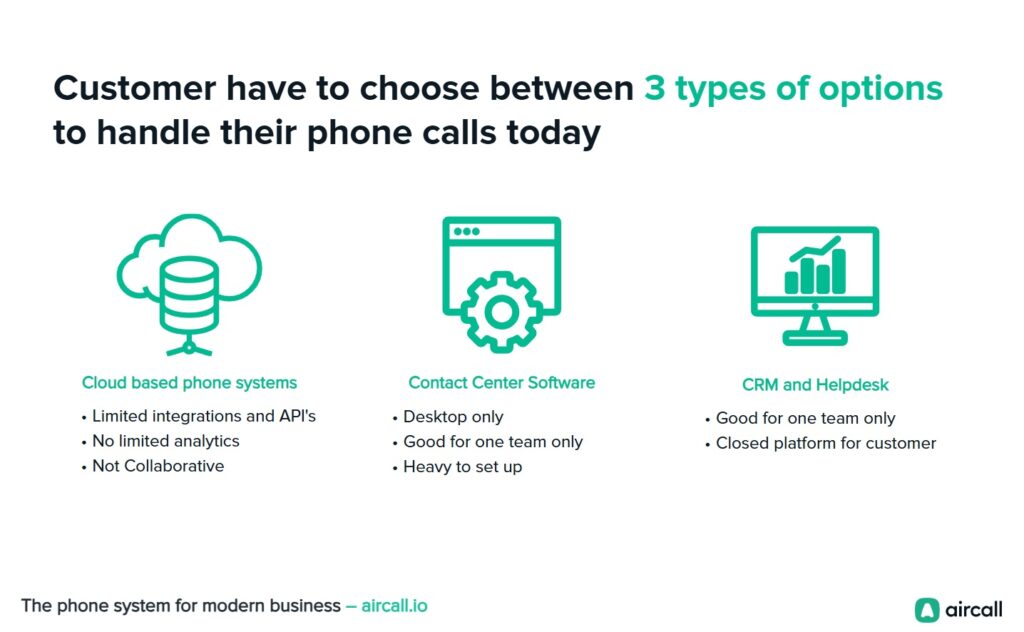
Aircall addressed communication inefficiencies that modern businesses face when managing customer interactions across multiple channels. Their statement emphasized how traditional phone systems couldn’t integrate with contemporary business software, creating data silos and reducing customer service effectiveness.
The presentation demonstrated understanding of evolving workplace dynamics, remote team coordination challenges, and the need for measurable communication analytics. They positioned poor integration capabilities as a significant competitive disadvantage for growing companies.
Uber

Uber‘s slide concentrated on urban transportation friction, highlighting the unreliability of existing taxi services and the inconvenience of car ownership in dense metropolitan areas. They presented specific scenarios where current transportation options failed customer expectations.
Key pain points included unpredictable wait times, inconsistent service quality, limited payment options, and lack of trip transparency. Their presentation established urban professionals as the primary target audience while demonstrating global scalability potential.
Youtube

YouTube identified content creators’ challenges in reaching audiences through traditional media channels, emphasizing the high barriers to entry and limited distribution options available before online video platforms. Their slide focused on democratizing content creation and distribution.
They highlighted how traditional broadcasting required significant capital investment, technical expertise, and industry connections. The statement positioned independent creators as an underserved market segment with substantial growth potential.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long should a problem slide be in a pitch deck?
A slide should contain 3-5 key pain points maximum, presented in bullet format or short paragraphs. Investors need sufficient detail to understand customer challenges without overwhelming information density. Focus on the most impactful issues that directly justify your solution approach.
What’s the difference between problem statement slide and pain points?
A statement slide defines the overarching issue your startup addresses, while pain points represent specific manifestations or symptoms of that broader challenge. Pain points provide concrete examples that make abstract issues tangible for investor audiences.
Should the problem slide include market size data?
Include 1-2 key market statistics that demonstrate issue scale, but reserve detailed market analysis for dedicated market opportunity slides. The presentation should establish that many customers experience this challenge, while later slides quantify the addressable market size and revenue potential.