Business Model Slide
The business model slide serves as the financial foundation of your pitch deck, acting as a bridge between your product vision and earnings reality. Market research shows 78% of investors consider the business model slide among the top three critical elements when evaluating startup potential. This slide clarifies not just what your company does, but how it generates sustainable revenue streams while maintaining competitive advantages. Within the framework of financial modeling, this slide transforms abstract product concepts into concrete economic mechanisms. Investors need clarity on how customer value translates into company proceeds, making this slide essential for conveying commercial viability. The business model slide establishes credibility by showing founders understand the economics behind their venture, addressing fundamental questions about unit economics and scalability.
Investor Expectations
Seasoned investors approach business model slides with specific analytical frameworks, seeking evidence of thorough market understanding and financial discipline. They meticulously examine earnings streams for diversity and sustainability, evaluating if the model can generate predictable cash flows. Scalability metrics receive particular scrutiny, as investors need confidence that revenue growth won’t demand proportional increases in operational complexity. Cost structure analysis is another cornerstone, assessing Customer Acquisition Costs (CAC), Lifetime Value (LTV) ratios, and operational expense scaling patterns. Depending on market conditions, investors may prioritize different metrics. The most sophisticated investors also evaluate competitive moats—like pricing power or network effects—that protect earnings streams and ensure long-term market positioning.
Business Model Slide Value
Strategic positioning within pitch presentations demands that business model slides tell compelling economic stories, not merely list revenue sources. The slide boosts investor confidence by demonstrating a founder’s grasp of market economics and ability to create sustainable competitive advantages. Well-crafted business model presentations highlight how customer problems translate into earnings opportunities while maintaining operational efficiency. Innovation in business model design often differentiates successful startups, so highlighting unique monetization approaches, novel pricing strategies, or creative revenue stream combinations is key. Ultimately, the slide must convey growth sustainability, showing clear paths for initial earnings streams to expand through customer retention, upselling, and market penetration.
Business Model Slide Creation
Build Your Slide
Constructing an effective business model slide begins with a compelling headline that concisely encapsulates your economic strategy. This headline should immediately signal your primary monetization approach and target market segment. When selecting a template, prioritize professional pitch deck templates that emphasize visual clarity over decorative elements. The template should accommodate multiple income streams without visual clutter, allowing investors to quickly grasp your economic model’s complexity and interconnections. The information hierarchy should flow logically from primary revenue sources to supporting economic elements.
Slide Content
Clearly defining your core economic components is vital. Core revenue streams require detailed explanations of pricing tiers, contract lengths, commission structures, or licensing arrangements. Economic model classification helps investors quickly understand your fundamentals; for example, SaaS companies should emphasize recurring income predictability, while marketplace businesses must demonstrate network effects. Finally, key cost insights provide essential context for revenue projections, covering detailed channel analysis for customer acquisition costs, scaling assumptions for operational expenses, and personnel costs for team expansion plans to make growth achievable.
Questions Your Slide Answers
Your slide must address investor concerns about sustainability and growth potential. Consider these critical questions:
- How do different revenue streams scale with customer acquisition?
- What are your Average Revenue Per Account (ARPA) calculations, ideally segmented by customer?
- How does your pricing model align with customer value propositions?
- What are your key cost drivers, and how will you maintain profitability? These questions demand specific numerical support and logical reasoning based on market conditions, helping to make your case solid.
Common Mistakes Avoid
Avoid common pitfalls that can undermine your pitch presentation. Don’t overwhelm investors with excessive detail; focus on the elements that drive 80% of your economic model’s performance. A lack of numerical support will undermine credibility; every income stream and cost structure needs specific metrics and benchmarks. Ignoring cost considerations creates unrealistic profitability projections. Furthermore, outlandish projections without market validation signal poor judgment. Finally, avoid text-heavy design; transform lengthy explanations into visual elements like flowcharts, graphs, and tables so investors can grasp your business model quickly.
Design Tips
Effective design significantly enhances comprehension. Use simple layouts that eliminate visual distractions, utilizing white space to separate revenue and cost categories. Incorporate high-quality graphics, such as flowcharts, pricing diagrams, and revenue visualizations, to transform complex business models into intuitive stories. Ensure readable fonts for accessibility across various presentation environments, maintaining a clear font size hierarchy. Lastly, consistent branding across all pitch deck elements—color schemes, logos, and design elements—creates a cohesive investor experience and should be a priority.
Business Model Slide Examples
Examining successful startups provides valuable insights into how to create effective business model slides:
- Airbnb’s slide effectively communicates marketplace economics through clear commission structures and emphasis on network effects (Source).
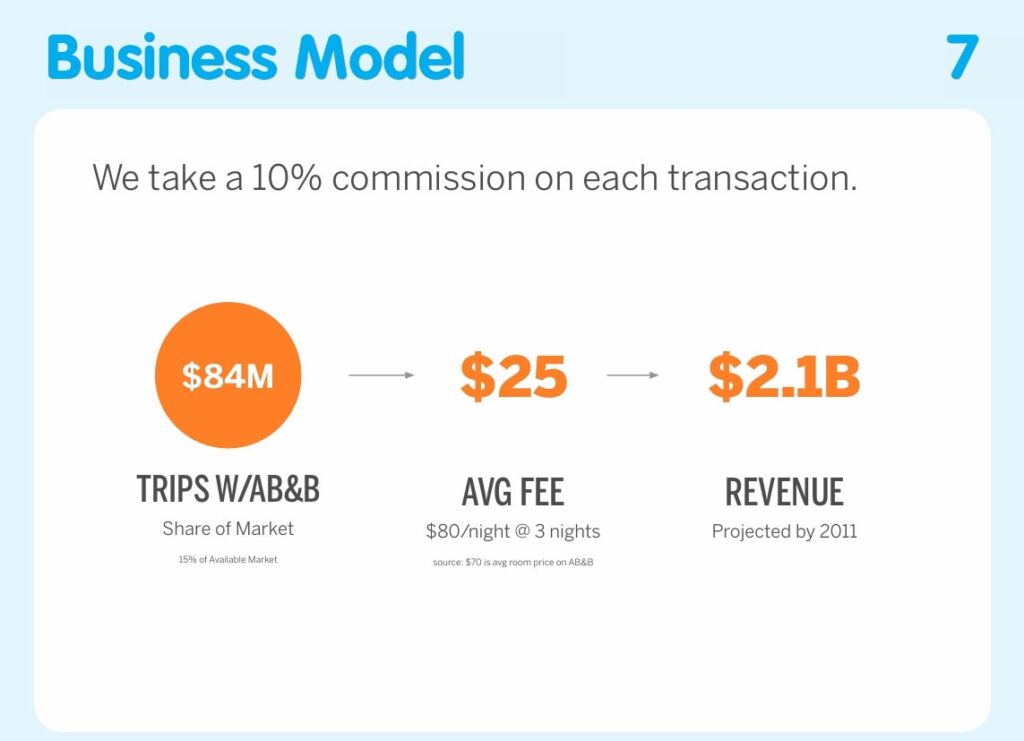
- Uber’s presentation focuses on transaction-based income with geographic scalability and operational efficiency (Source).

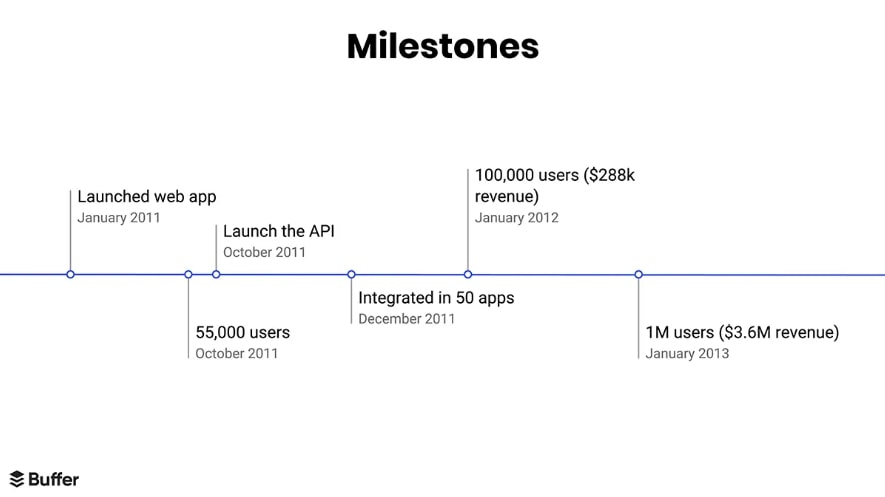
- Buffer’s SaaS model exemplifies subscription business best practices, segmenting customer tiers and demonstrating upgrade paths (Source).
Pitch Deck Integration
Business model slides must seamlessly integrate with other pitch deck elements to create a coherent investor narrative. The problem slide establishes market pain points that your business model specifically addresses. Solution slides introduce product capabilities that the business model effectively monetizes. Market slides provide essential context for business model scalability. Traction slides validate business model assumptions through actual performance metrics. Finally, financial projection slides build upon your business model’s foundation with detailed earnings forecasting and profitability timelines. Your pitch should tell a unified story.
Overall Pitch Deck Improvement
To enhance your entire pitch deck:
- Problem definition slides should require customer research validation.
- Team slides must demonstrate relevant experience for executing the presented business model.
- Financial projections should include conservative scenario planning alongside optimistic growth cases.
- Competition analysis should focus on business model differentiation, translating into sustainable revenue protection.
Pitch Deck Slide Key Integration Points
Here are some of these:
| Pitch Deck Slide | Key Integration Points | Business Model Connection |
| Problem | Market pain quantification | Revenue opportunity validation |
| Solution | Value proposition clarity | Monetization justification |
| Market | TAM/SAM calculations | Scalability assumptions |
| Competition | Differentiation factors | Pricing power analysis |
| Traction | Performance metrics | Model validation evidence |
| Team | Execution capability | Scaling experience |
| Financials | Revenue projections | Unit economics scaling |
| Investment | Capital requirements | Growth milestone funding |