Startup Financial Model Templates: Free & Paid
The financial model serves as the backbone of any SaaS operation, transforming raw data into actionable intelligence. Market research data confirms that startups with structured financial planning achieve 30% higher growth rates compared to those operating without systematic forecasting frameworks.
Why a SaaS Financial Model Matters
Finance leaders leverage comprehensive models to decode complex business relationships and identify optimization opportunities. A robust SaaS financial model connects customer acquisition cost with lifetime value, revealing the true unit economics that drive sustainable growth. Within the framework of financial modeling, executives can pinpoint which customer segments generate the highest margins and adjust resource allocation accordingly.
Strategic Growth Driver
The model transforms scattered data points into cohesive insights. When customer churn increases by 2%, the model immediately calculates the downstream impact on:
- Revenue projections
- Cash flow requirements
- Hiring plans
This interconnected approach enables proactive decision-making rather than reactive problem-solving.
Investor Confidence Builder
Investors evaluate hundreds of pitches monthly, making first impressions crucial for funding success. A well-structured financial model with detailed projections demonstrates management’s understanding of their business fundamentals. Professional investors specifically look for models that accurately reflect SaaS metrics including:
- Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR)
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
- Lifetime Value (LTV) ratios
The visual presentation through dynamic charts and scenario analysis showcases the startup’s potential under various market conditions. Venture capitalists report that startups with sophisticated financial models receive 40% more follow-up meetings during the due diligence process. The model serves as a communication tool that translates business vision into quantifiable outcomes.
Internal Decision Sandbox
Financial models function as testing environments where teams can experiment with different strategies without real-world consequences.
- Product managers can model the impact of feature releases on customer retention.
- Sales leaders can forecast how pricing changes affect conversion rates and overall revenue.
This sandbox approach proves particularly valuable when evaluating trade-offs between customer acquisition strategies. The model can simulate scenarios where marketing spend increases by 50% while comparing the resulting customer growth against alternative investments in product development or customer success initiatives. Teams gain clarity on resource allocation decisions through data-driven analysis rather than intuition alone.
Top Startup Financial Models
The financial modeling landscape offers diverse solutions ranging from free templates to comprehensive paid platforms. Each option addresses specific business needs and complexity levels.
SaaS Financial Plan 2.0 by Christoph Janz
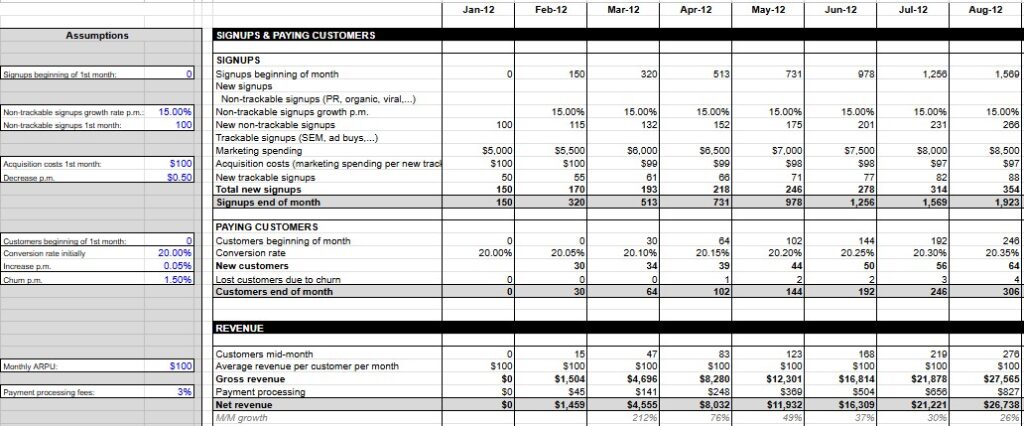
Christoph Janz’s template stands out for its clean design and SaaS-focused approach. The model incorporates essential metrics including monthly recurring revenue, churn rates, and customer acquisition costs with intuitive input fields. Its strength lies in the clear visualization of key performance indicators through automated charts and dashboards.
However, the template’s limitations become apparent for growing businesses:
- The 2-year forecast horizon restricts long-term strategic planning.
- The monthly subscription modeling doesn’t accommodate annual or multi-year contracts effectively.
- The absence of a balance sheet component limits its utility for comprehensive financial reporting.
- Last updated in 2019, it may not reflect current SaaS industry practices.
Download SaaS Financial Plan 2.0 от Christoph Janz
Standard SaaS Financial Plan by Ben Murray
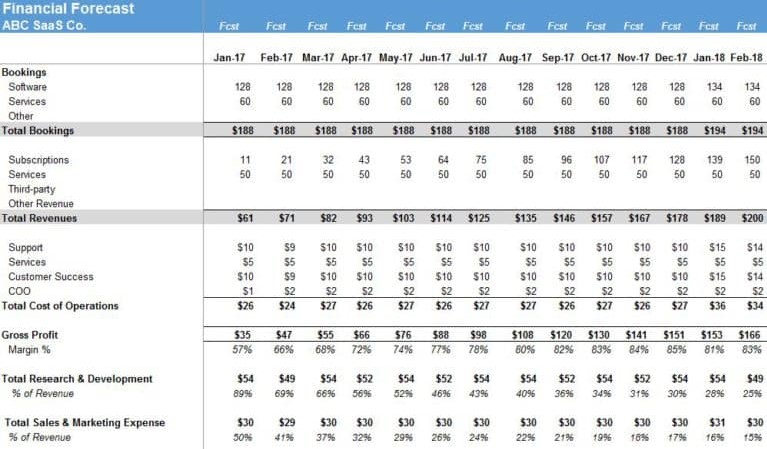
Ben Murray’s model offers more sophisticated cost modeling compared to Janz’s template. The framework accommodates various contract structures including:
- Monthly
- Annual
- Custom commitment terms
Customer acquisition modeling includes multiple channels with distinct conversion rates and costs, providing granular insights into marketing effectiveness. The template extends forecasting to 5 years and includes actual versus projected comparison capabilities. Service revenue components beyond subscription fees receive dedicated modeling sections. Among free templates, this option provides the most comprehensive approach to SaaS financial planning, though it requires more initial setup time than simpler alternatives.
More about Standard SaaS Financial Plan от Ben Murray
FISY Innovation Plan by Remi Berthier
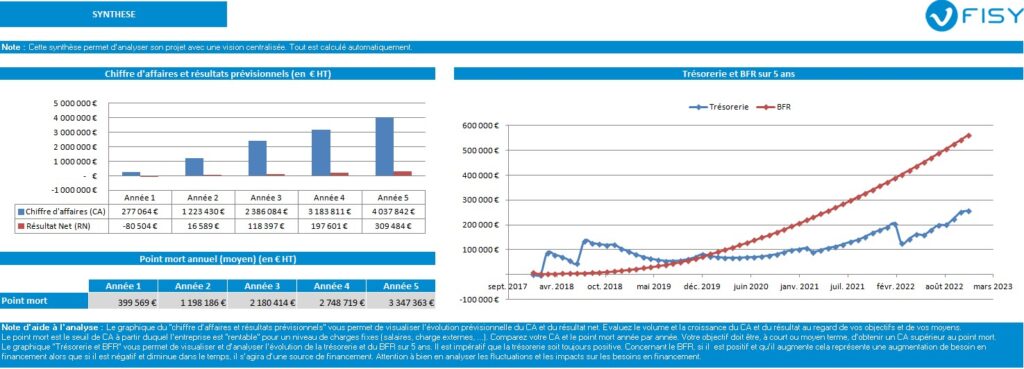
This French-focused template prioritizes ease of use over advanced analytical capabilities. The model includes specific provisions for French tax incentives including:
- Crédit d’Impôt Recherche (CIR)
- Jeune Entreprise Innovante (JEI) status
These features make it particularly valuable for French entrepreneurs navigating local regulatory requirements. The template’s customization options allow adaptation to various business models within the innovation ecosystem. However, its analysis capabilities remain limited compared to more comprehensive solutions. The simplified approach works well for early-stage planning but may require upgrading as business complexity increases.
Download FISY Innovation Plan от Remi Berthier
Causal by Taimur and Lukas
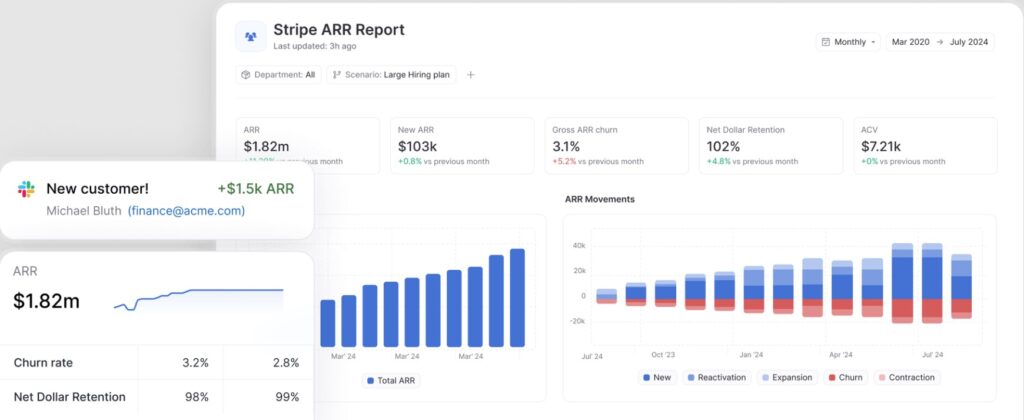
Causal represents a modern approach to financial modeling, designed to replace traditional spreadsheet-based planning. The platform offers real-time data connections, eliminating manual update requirements that plague Excel-based models. The interface supports:
- Collaborative editing
- Version control
- Audit trails
Built-in templates include contributions from industry experts like Taylor Davidson. The platform’s strength lies in its ability to handle complex scenarios and sensitivity analysis through automated calculations. For teams requiring sophisticated modeling capabilities with minimal Excel expertise, Causal provides a compelling alternative to traditional templates.
SaaS Financial Model 3.0 by Baremetrics
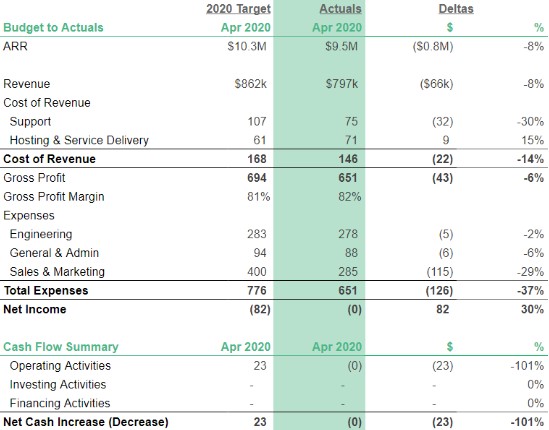
Baremetrics emphasizes the “Autopilot” philosophy, creating models that require minimal ongoing maintenance once properly configured. The template includes comprehensive financial statements covering:
- Profit and loss
- Cash flow
- Balance sheet projections over 5 years
This three-statement approach provides the complete financial picture required for investor presentations and board reporting. The model excels in SaaS-specific metrics analysis with automated chart generation for key performance indicators. Scenario building capabilities allow comparison of different growth strategies and market conditions. The template’s weakness appears in complex pricing model scenarios where multiple product tiers and add-on services require extensive customization.
SaaS: SME & Users by Alexander Jarvis
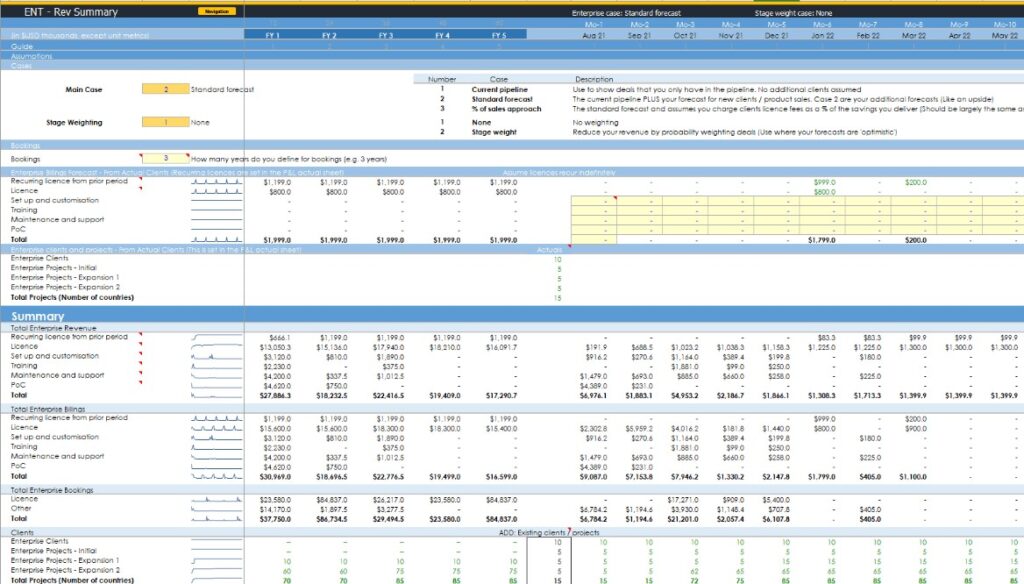
This premium template ($319 basic, $1299 advanced) delivers enterprise-level modeling capabilities for serious SaaS businesses. The advanced version includes sophisticated customer lifecycle modeling with upgrade, downgrade, and churn pathways that reflect real-world customer behavior patterns. Acquisition channel modeling supports multiple marketing streams with distinct economics.
The template provides over 50 automated charts and dashboards covering advanced SaaS metrics including:
- Net dollar retention
- Expansion revenue
- Cohort analysis
Cost modeling ties directly to operational metrics, enabling precise budget planning. The basic version omits some financial statement components, limiting its usefulness for comprehensive reporting needs.
Visit Alexander Jarvis (SaaS Financial Model)
Liveplan by Palo Alto Software
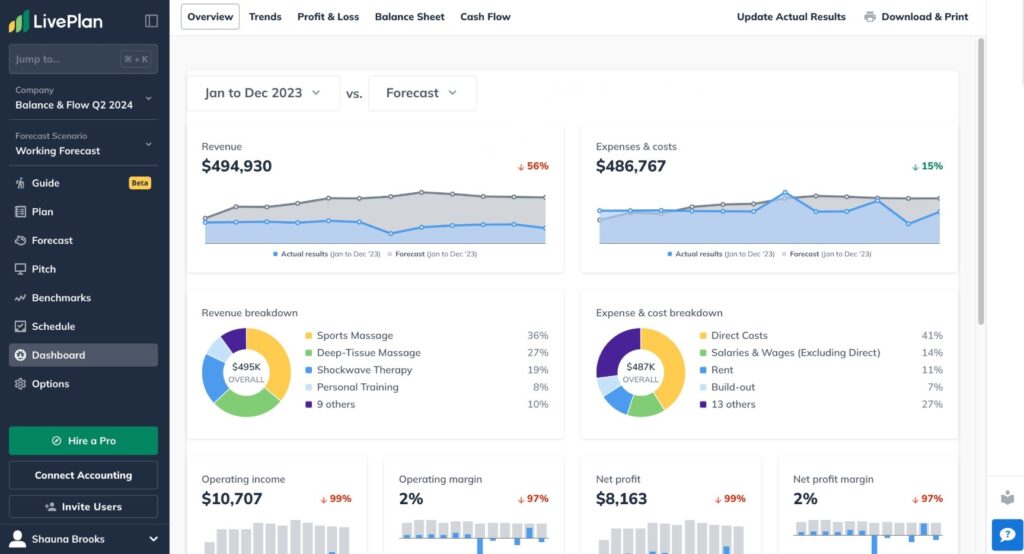
Liveplan offers more granular revenue control compared to competitors like EY Finance Navigator. The platform supports various revenue recognition patterns including:
- Recurring subscriptions
- Billable hours
- One-time transactions
Payment terms modeling accommodates different collection scenarios and cash flow timing. Hardware revenue components receive dedicated modeling attention, making it suitable for SaaS companies with physical product elements. However, the platform lacks SaaS-specific features like automated churn modeling and cohort analysis. Customer input requires manual entry rather than formula-driven calculations, increasing maintenance overhead.
Visit Palo Alto Software (Liveplan)
Slidebean Financial Model Template
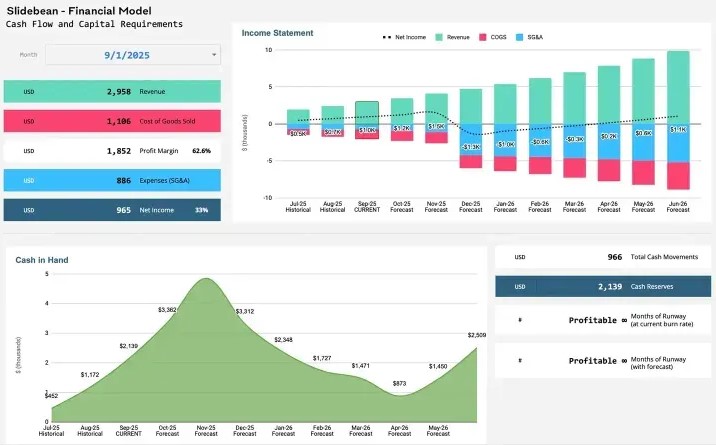
Slidebean’s solution combines template functionality with expert support services. The platform covers:
- Revenue projections
- Expense planning
- Fundraising scenarios through automated calculations
A comprehensive knowledge base provides guidance for common modeling challenges. Over 30,000 companies utilize Slidebean’s templates, indicating market validation for their approach. The platform offers both SaaS-specific and general startup models with customization options. Expert analyst support provides professional review and optimization suggestions, particularly valuable for teams lacking deep financial modeling experience.
Download Slidebean Financial Model Template
Graphite Financial Startup Model
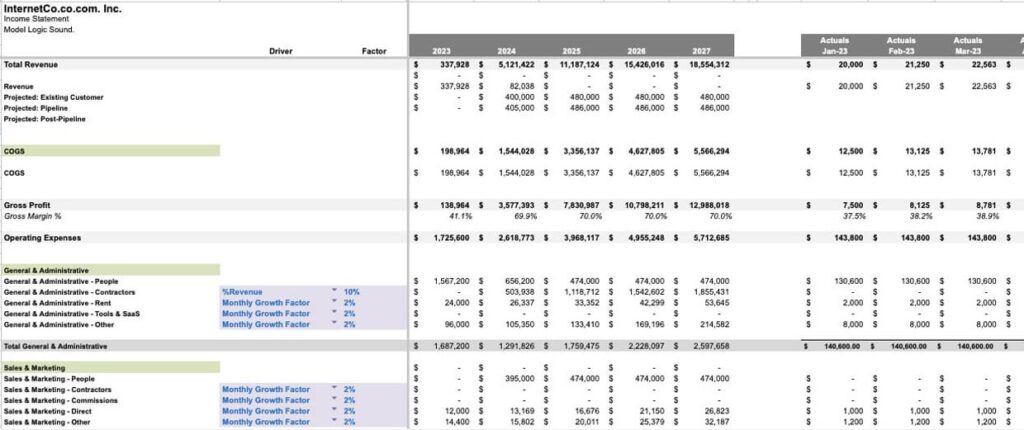
Graphite delivers a clean three-statement model designed specifically for board presentations and investor communications. The template includes built-in error checking mechanisms that identify common modeling mistakes before they impact projections. Both SaaS and consumer packaged goods versions address different business model requirements.
The structure prioritizes clarity and professional presentation over advanced analytical features. Customizable modules allow adaptation to specific industry needs while maintaining the core financial statement integrity. This approach works well for founders seeking investor-ready materials without extensive financial modeling expertise.
Download Graphite Financial Startup Model
Ramp Startup Financial Model
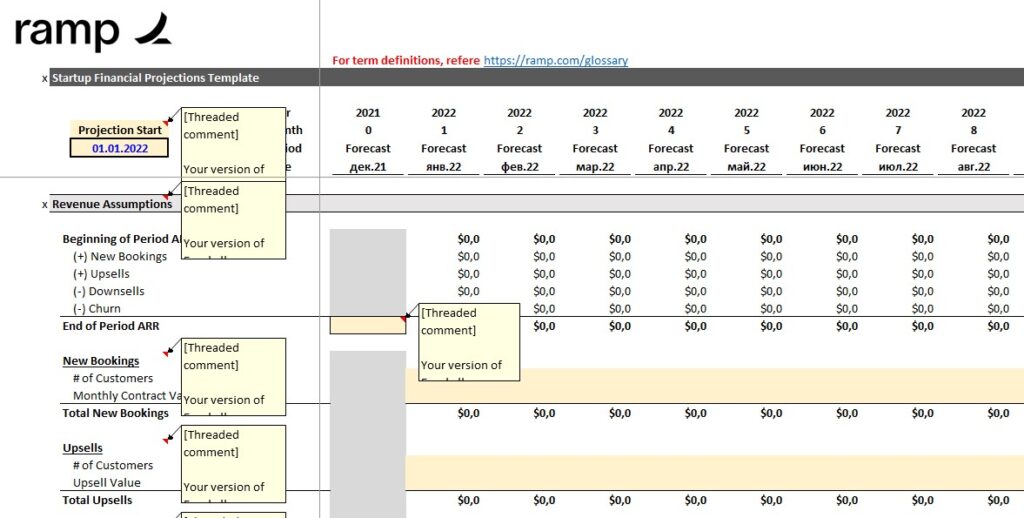
Ramp provides a free three-statement model with user-friendly design principles. The template includes:
- Staff planning
- Expense management features with dynamic summary reporting
Cash runway analysis helps early-stage startups understand funding requirements and timeline constraints. While optimized for B2B SaaS structures, the model adapts to other business types through configuration changes. The template serves early-stage companies needing basic projection capabilities without overwhelming complexity. Its strength lies in simplicity and accessibility rather than advanced analytical features.
Zeni Startup Financial Model Template
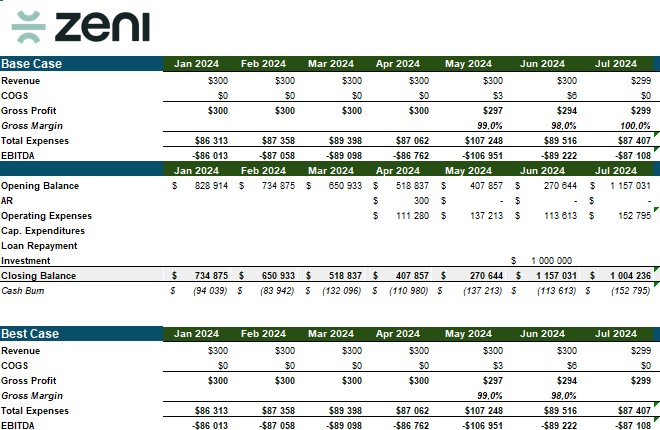
Zeni focuses on VC-ready financial projections with dedicated setup support for complex business logic requirements. The template accommodates diverse business models through customizable frameworks while maintaining investor-standard reporting formats. Scenario-based projections enable comparison of different strategic approaches.
The platform provides implementation support to ensure proper model configuration from the outset. This guided approach reduces common setup errors that compromise projection accuracy. The template works particularly well for startups in active fundraising phases or early operational stages requiring professional-grade financial planning.
Download Zeni Startup Financial Model Template
How to Use a SaaS Financial Model Template
Implementing a financial model template requires a systematic approach and attention to data quality. The process transforms raw business assumptions into structured projections that guide strategic decisions.
Step-by-Step Guide
- Begin by downloading or accessing your chosen template and reviewing its structure completely before inputting any data.
- Most templates organize information into distinct sections covering assumptions, calculations, and outputs. Understanding this flow prevents errors that compound throughout the model.
- Create a data collection checklist covering historical financial performance, current metrics, and future assumptions.
- Input data methodically, starting with historical information and progressing through current metrics to future projections.
- Review each section’s calculations before moving forward, as errors in early sections cascade through subsequent analyses.
- Test the model with known scenarios to verify calculation accuracy and logical consistency.
Inputting Key Data
- Templates typically use color coding to distinguish input cells from calculation cells.
- Yellow or blue cells commonly indicate areas requiring user input, while white or gray cells contain formulas that should not be modified. This visual system prevents accidental formula corruption that compromises model integrity.
- Start with basic business information including company details, fiscal year dates, and reporting currency.
- Progress to historical financial data covering at least 12 months of actual performance where available.
- Input current operational metrics including customer counts, average contract values, and churn rates.
- Revenue assumptions require particular attention to growth rates, pricing strategies, and market penetration expectations.
- Cost assumptions should reflect both variable costs that scale with revenue and fixed costs that remain stable regardless of growth.
- Review all inputs for reasonableness and consistency with industry benchmarks before generating reports.
Excel Templates: Strengths & Weaknesses
Excel-based financial models dominate the startup ecosystem due to accessibility and flexibility. However, their limitations become apparent as businesses scale and complexity increases.
Initial Utility
Excel templates provide immediate value for early-stage startups with limited financial modeling expertise.
- The familiar interface reduces learning curves compared to specialized software platforms.
- Templates offer cost-effective solutions for basic forecasting needs without monthly subscription requirements.
- Customization capabilities allow adaptation to specific business models and reporting requirements. Teams can modify formulas, add new metrics, and adjust formatting to match their operational needs.
- Excel’s calculation power handles complex scenarios and sensitivity analysis through built-in functions and add-ins. Goal seek and solver tools enable optimization analysis for strategic decision-making.
- The platform’s ubiquity ensures compatibility across different operating systems and sharing environments.
Scalability Challenges
Excel’s limitations emerge as businesses grow beyond simple financial planning needs.
- Manual data entry increases error probability, particularly when multiple team members contribute to model updates.
- Version control becomes problematic when several stakeholders maintain separate copies with conflicting information.
- Complex SaaS businesses with multiple product lines, customer segments, and revenue streams strain Excel’s organizational capabilities.
- Formula auditing becomes difficult in large models, making error detection and correction time-consuming.
- Real-time data integration requires manual processes that delay decision-making and increase maintenance overhead.
- Collaboration suffers in Excel environments where simultaneous editing creates conflicts and data loss risks.
- Advanced analytics including cohort analysis, predictive modeling, and automated reporting exceed Excel’s native capabilities without extensive macro development.
These limitations drive many growing startups toward specialized financial planning platforms as their operations mature.